BMI Calculator
BMI introduction
BMI is a measurement of a person's leanness or corpulence based on their height and weight, and is intended to quantify tissue mass. It is widely used as a general indicator of whether a person has a healthy body weight for their height. Specifically, the value obtained from the calculation of BMI is used to categorize whether a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese depending on what range the value falls between. These ranges of BMI vary based on factors such as region and age, and are sometimes further divided into subcategories such as severely underweight or very severely obese. Being overweight or underweight can have significant health effects, so while BMI is an imperfect measure of healthy body weight, it is a useful indicator of whether any additional testing or action is required. Refer to the table below to see the different categories based on BMI that are used by the calculator
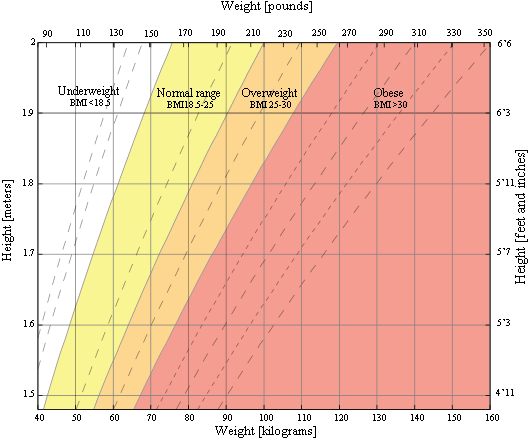
BMI chart for adults
This is a graph of BMI categories based on the World Health Organization data. The dashed lines represent subdivisions within a major categorization.
BMI table for children and teens, age 2-20
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends BMI categorization for children and teens between age 2 and 20.
|
Category
|
Percentile Range
|
|
Underweight
|
<5%
|
|
Healthy weight
|
5% - 85%
|
|
At risk of overweight
|
85% - 95%
|
|
Overweight
|
>95%
|
BMI formula
Below are the equations used for calculating BMI in the International System of Units (SI) and the US customary system (USC) using a 5'10", 160-pound individual as an example:
BMI = 703 × mass (lbs) height2 (in) = 703 × 160 702 = 22.96 kg m2
BMI = mass (kg) height2 (m) = 72.57 1.782 = 22.90 kg m2
BMI Prime
BMI prime is the ratio of a person's measured BMI to the upper limit of BMI that is considered "normal," by institutions such as the WHO and the CDC. Though it may differ in some countries, such as those in Asia, this upper limit, which will be referred to as BMIupper is 25 kg/m2.
The BMI prime formula is:
|
BMI prime =
|
BMI 25
|
Since BMI prime is a ratio of two BMI values, BMI prime is a dimensionless value. A person who has a BMI prime less than 0.74 is classified as underweight; from 0.74 to 1 is classified as normal; greater than 1 is classified as overweight; and greater than 1.2 is classified as obese. The table below shows a person's weight classification based on their BMI prime:
|
Classification
|
BMI
|
BMI Prime
|
|
Severe Thinness
|
< 16
|
< 0.64
|
|
Moderate Thinness
|
16 - 17
|
0.64 - 0.68
|
|
Mild Thinness
|
17 - 18.5
|
0.68 - 0.74
|
|
Normal
|
18.5 - 25
|
0.74 - 1
|
|
Overweight
|
25 - 30
|
1 - 1.2
|
|
Obese Class I
|
30 - 35
|
1.2- 1.4
|
|
Obese Class II
|
35 - 40
|
1.4 - 1.6
|
|
Obese Class III
|
> 40
|
> 1.6
|
BMI prime allows us to make a quick assessment of how much a person's BMI differs from the upper limit of BMI that is considered normal. It also allows for comparisons between groups of people who have different upper BMI limits.
Ponderal Index
The Ponderal Index (PI) is similar to BMI in that it measures the leanness or corpulence of a person based on their height and weight. The main difference between the PI and BMI is the cubing rather than squaring of the height in the formula (provided below). While BMI can be a useful tool when considering large populations, it is not reliable for determining leanness or corpulence in individuals. Although the PI suffers from similar considerations, the PI is more reliable for use with very tall or short individuals, while BMI tends to record uncharacteristically high or low body fat levels for those on the extreme ends of the height and weight spectrum. Below is the equation for computing the PI of an individual using USC, again using a 5'10", 160-pound individual as an example:
PI = height (in) ∛mass (lbs) = 70 ∛160 = 12.89 in ∛lbs
PI = mass (kg) height3 (m) = 72.57 1.783 = 12.87 kg m3